Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is a powerful technology used in network communication that helps users inspect and analyze data packets in transit. The inspection identifies specific types of traffic, applications, and even individual users.
We can use DPI for many things, including network security, traffic management, and content filtering. However, its use often results in concern over privacy, censorship, and net neutrality.
This article will explore the basics of DPI, how it works, potential risks and concerns, and whether VPN users should be concerned.
What is Deep Packet Inspection?
Imagine you're sending a letter in the mail. The outside of the envelope tells the post office where to send it, but they can't see what's inside it. Deep Packet Inspection is like opening an envelope and reading the letter's contents.
In computer networks, we send information in small packets. Deep Packet Inspection technology allows network administrators to read the information inside these packets. The information can include data types, sender and recipient information, or specific content.
By analyzing the contents of these packets, network administrators can gain insights into network usage and identify potential security threats or performance issues. For example, they can detect if someone is trying to transmit a virus or hack into the network, or they can monitor which websites employees are accessing.
How Deep Packet Inspection Works
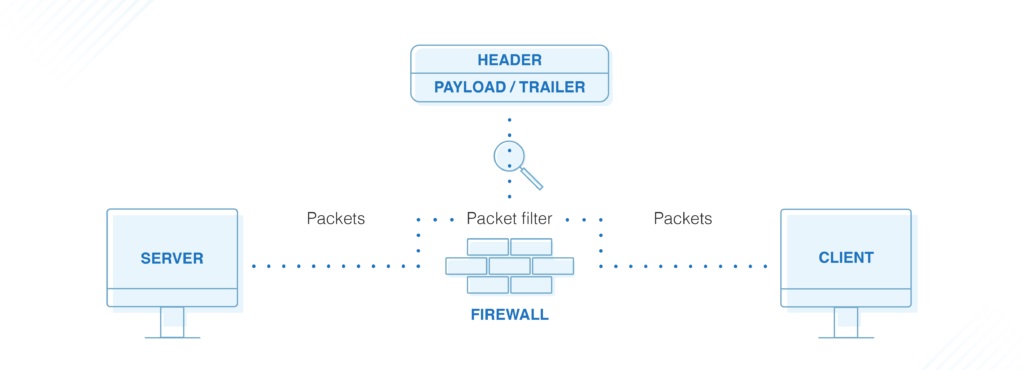
There are three distinct stages of operation in Deep Packet Inspection; Packet Decoding, Signature Analysis, and Packet Filtering. These three stages of DPI work together to provide a comprehensive view of network traffic.
Packet Decoding
The first stage of DPI is packet decoding. Think of this as opening the envelope of a letter and looking at what's inside. When the network receives a data packet, it is first decoded to reveal its content. This process involves breaking down the packet into its component parts and identifying the type of data it contains, such as text, images, audio, or video.
Signature Analysis
The second stage of DPI is called signature analysis. This stage involves comparing the contents of the packet to a database of known signatures or patterns of data associated with specific types of network traffic, such as emails, web browsing, or file transfers.
If the packet matches a known signature, it can then be classified. If there is no match, it is flagged for further analysis, as it may contain new or previously unknown network traffic.
Packet Filtering
The final stage of DPI is packet filtering. In this stage, packet contents undergo analysis. This process helps determine whether they comply with network security policies or other rules the network administrator establishes.
If the packet violates these policies or rules, it is blocked or redirected to a quarantine area for further investigation. The packet can pass through the network and reach its intended destination if it is deemed safe and compliant.
Deep Packet Inspection and Internet Censorship

One of the main concerns about DPI technology is its use by governments to monitor, control, or censor internet activity. We know that DPI enables strict Internet controls in various countries, including China, Russia, and Iran.
China
China uses DPI extensively to control and censor internet activity. The Chinese government uses the Great Firewall of China, which employs DPI, to block access to websites and services deemed politically sensitive or inappropriate.
For example, social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram are all blocked in China, and access to news websites like The New York Times and BBC is restricted.
Russia
The Russian government also uses DPI to monitor and control internet activity within its borders. The government uses DPI to block access to websites and services deemed politically sensitive or inappropriate.
For example, social media platforms such as LinkedIn and Telegram are not available in Russia, and access to news websites such as The Guardian and The New York Times is restricted.
Iran
The Iranian government also uses DPI to monitor and control internet activity within its borders. Iran's National Internet Network uses DPI to block access to websites and services deemed immoral or politically subversive.
It's worth noting that using DPI for internet censorship and surveillance is controversial and raises significant concerns about privacy, free speech, and human rights. Many experts argue that DPI can be used to violate these fundamental rights and should be subject to greater scrutiny and oversight.
How to Avoid Deep Packet Inspection With a VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) can help avoid DPI by encrypting the data transmitted over the network. When you use a VPN, your data is encrypted and sent through a secure tunnel to the VPN server.
This encryption process means that any DPI tools trying to analyze the data packets will only see encrypted data. Anyone trying to make sense of the data will only be successful with the appropriate decryption key.
However, it's worth noting that governments can use DPI in other ways. For example, they may opt to detect and block all VPN traffic without trying to decipher data. In these cases, all the DPI system must achieve is to identify the encrypted data packets.
Here are some areas that can help you choose a better VPN for better DPI Avoidance;
Obfuscation or Stealth Technology
Obfuscation or stealth technology helps to hide your VPN traffic from your ISP and prevent them from detecting and blocking it. Some VPN providers offer this feature, so choose one that does. NordVPN offers server obfuscation, while Surfshark has a similar feature called Camouflage mode.
Support for Multiple Protocols
Most VPNs use the OpenVPN protocol by default, often easily detectable by DPI. However, some VPNs support multiple protocols, such as IKEv2, L2TP/IPSec, and SSTP, which can be more difficult for ISPs to detect.
Large Server Networks
A VPN with an extensive server network can help you avoid DPI by allowing you to switch to a different server if one is detected and blocked by your ISP. Some VPNs with notably large server networks include CyberGhost and NordVPN.
Beware of Expanding Internet Censorship
A VPN can be an effective way to avoid DPI in many cases, but it's not a foolproof solution and may only work in some situations. It's essential to consider the specific circumstances and potential risks before relying on a VPN to avoid DPI.
Some countries may have laws and regulations prohibiting VPN use or making it difficult to use them effectively. Using a VPN to avoid DPI may be risky or illegal in these cases.