Biometrics uses unique physical or behavioral characteristics to verify a person's identity. Biometric authentication methods have become increasingly popular as they offer a convenient and secure way to authenticate individuals.
Biometric data is the digital representation of a person's biometric characteristics stored in a system for identification and verification purposes. However, using biometric data has raised concerns about its safety, as it is personal and sensitive information.
In this article, we will explore biometrics, the different types of biometric data, and whether or not biometric data is safe.
The Basics of Biometrics

Biometrics uses unique physical or behavioral characteristics to verify a person's identity. Biometric authentication methods use an individual's biometric data to authenticate them, rather than traditional methods such as passwords or PINs.
Biometric authentication methods can include fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, iris recognition, voice recognition, and behavioral recognition, such as the way a person types on a keyboard.
Biometrics are unique to an individual and cannot be replicated, making it a highly secure authentication method. Biometric authentication methods are also convenient, as users do not have to remember passwords or carry physical authentication devices such as smart cards or tokens.
Is Our Biometric Data Safe?
Although biometrics technology is safe in principle, like many other technologies, there are both technical and human loopholes. These have given rise to concerns about the safety of biometric data at government levels.
This data is sensitive information that, if compromised, can result in severe consequences. Unlike passwords, which you can change, biometrics are permanent and difficult to alter. If an attacker gains access, they can use it to impersonate you and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or facilities.
Some known risks to our biometric data include the following;
Biometric Data is at Risk of Theft
One of the significant risks associated with using biometric data is its potential for theft. We usually keep biometric data in a database, and if a data breach occurs, the biometric data of millions of individuals can be compromised.
Suppose a biometric system is poorly designed or implemented. In that case, it can be vulnerable to attacks, such as spoofing or replay attacks, which can compromise the accuracy and reliability of the system.
Potential for Misuse
Another concern is using biometric data for surveillance. Governments and private organizations increasingly use biometric technology for surveillance and tracking purposes, raising concerns about privacy and civil liberties.
We can also use biometric data to monitor individuals' movements, track their activities, and identify their location, which can be intrusive and violate their privacy rights. China is an excellent example of a country where the government leverages biometric data to monitor its citizens.
Security Incidents Involving Biometrics
Sadly, several biometric security breaches have happened over the years, like many security tools. Several have been significant;
Shanghai Police Data Theft (2022)
Hackers allegedly stole a database from the Shanghai police department. The database held over a billion Chinese citizens' particulars, including biometric data. It was later posted for sale as 23TB of data for approximately $200,000. (Source: Biometric Update)
Biostar Fingerprint Leak (2019)
In the 2019 Biostar 2 data breach, hackers went after a security platform owned by the South Korean biometrics company Suprema. They stole over 23 gigabytes of data, including biometric information such as fingerprints, facial recognition data, and unencrypted usernames and passwords. (Source: The Verge)
US Border Patrol Data Breach (2019)
A US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) subcontractor suffered a data breach in 2019, which resulted in the theft of over 100,000 photos, license plate numbers, and some biometric data, such as facial recognition data. (Source: Washington Post)
UK Biometric Data Breach (2017)
The UK's Metropolitan Police suffered a data breach in 2017, which resulted in the theft of data, including fingerprints, of over 1,000 people. Also involved in the incident were banks and other companies. (Source: ZDNet)
How a VPN Helps Improve the Security of Biometric Data
Stay Safe Online With NordVPN
NordVPN offers over 5,500 secure servers protecting your data with military-grade encryption, a kill switch, and an audited no-logs policy.
A VPN can improve biometric data security by encrypting data, providing anonymity, securing connections, and bypassing geo-restrictions. However, it is crucial to choose a reputable VPN provider and follow best practices for data security.
VPNs help protect your biometric data with a series of security features, including;
- Encryption – VPNs encrypt all data transmitted between your device and the VPN server, making it difficult for hackers to intercept or access biometric data.
- Anonymity – VPNs hide your IP address and location, making it harder for attackers to target you or your biometric data.
- Secure connections – VPN services build a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the VPN server, protecting biometric data from interception.
- Geo-restriction bypass – In some cases, biometrics may be subject to geo-restrictions. A VPN can help bypass these restrictions, allowing you to access biometric systems (like your online banking) anywhere.
We Recommend NordVPN as one of the best services that can help you boost the security of your biometric data. It is one of the most highly-rated VPN services specializing in privacy and protection for your devices and data.
NordVPN also offers other security features, such as a kill switch, which can automatically disconnect your device from the internet if the VPN connection is lost, preventing any unencrypted data from being transmitted.
NordVPN also has a strict no-logs policy, meaning it does not store any data related to your online activity or biometric data.
How Biometrics Works in the Real World
Because of the highly personal nature of biometrics, it is especially relevant to security, monitoring, and tracking applications. It can quickly help to authenticate individuals and protect sensitive information or assets.
Some current use cases of biometrics include;
Securing Bank Transactions
Biometric authentication is becoming more common in the banking industry, with many banks using fingerprint or facial recognition systems to verify customer identities for digital transactions.
For example, Barclays Bank in the UK allows customers to use voice recognition or fingerprint scanning to access their accounts, conduct payments, and perform other secure transactions.
Smartphone and Other Device Access
Biometrics can control access to secure areas or authenticate individuals for enhanced security. The best example is any modern smartphone that supports on-device fingerprints or facial recognition.
Identity Verification in Law Enforcement
Some law enforcement agencies use biometric technologies to identify suspects or verify the identity of individuals, such as in criminal investigations or border control. For example, police in India use a biometric system called Automated Fingerprint Identification System (AFIS) to match fingerprints found at crime scenes with those in a database of known criminals.
Personalized Healthcare Control
We also use biometrics in healthcare settings to verify patient identity, monitor vital signs, and manage medical records. For example, the US National Center for Biotechnology Information moots fingerprint scanning to identify patients correctly before medical treatment.
Customs and Immigration Clearance
Biometrics are used in immigration and border control to identify travelers and prevent fraud. Many airports now use biometric technologies such as facial recognition or iris scanning to verify the identity of travelers and improve security.
For example, the US Customs and Border Protection agency has implemented facial recognition systems at many US airports to speed up the entry process for travelers.
Why is The Use of Biometrics Increasing?
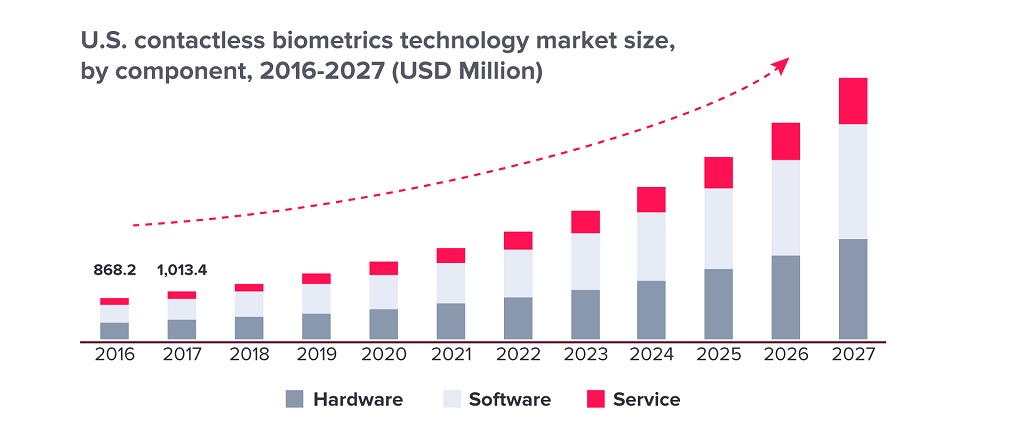
Using biometrics is on a positive growth path, especially in the US and China. We also consider biometric data more secure than traditional forms of identification, such as passwords or PINs, because it is unique to each individual and cannot be easily replicated or shared.
Moreover, biometric authentication is more convenient and faster than traditional forms of identification, as it only requires the user to present their biometric data, such as a fingerprint or facial recognition, to gain access.
Other advantages include;
Improved accuracy
Biometric technologies have improved significantly in recent years, making them more accurate and reliable. This system has increased confidence in its use for security and authentication purposes.
More Convenience
Biometric authentication can be more convenient than traditional passwords or PINs. Users don't have to remember complex passwords or carry physical tokens like key cards or fobs.
Enhanced Cost-effectiveness
Biometric technologies have become more affordable in recent years, making them more accessible to organizations of all sizes. These cost savings have led to their increased adoption in various applications.
Most Common Types of Biometric Data
There are several types of biometric data, each with its unique characteristics. The most common types of biometric data include;
Fingerprints
Fingerprint recognition is common today. It involves using a digital or physical scanner to capture an image of the unique pattern of ridges and valleys on your fingertip. Fingerprint biometrics are commonly used in access control systems, mobile device authentication, and border control.
Facial Recognition
In facial recognition, cameras capture an image of your face and then compare it to a stored database of faces to confirm your identity. Facial recognition is used in security systems, mobile device authentication, and law enforcement.
Iris Recognition
This form of biometrics goes beyond facial recognition but uses a similar concept. A camera captures an image of your iris, the colored part of your eye, and compares it to a stored database of irises to confirm your identity.
Voice Recognition
This biometrics system uses software to analyze your voice patterns and compare them to a stored database of voices. Voice recognition is used in mobile device authentication, banking and finance, and customer service.
Behavioral Biometrics
This system analyzes behavior patterns, such as typing or mouse movements, to confirm a person's identity. Some phone apps offer behavioral biometrics to anticipate your typing input for improvements to speed and accuracy.
Final Thoughts – Improve Your Biometric Data Security With a VPN
Biometric data is becoming an increasingly common form of personal identification. It is essential to understand the potential security risks associated with its use. While biometric data can offer high security and convenience, it is also vulnerable to data breaches and unauthorized access.
Ultimately, while biometric data security is complex, securing personal information, including biometric data, is critical in the digital age. A VPN can be a valuable tool in protecting biometric data and maintaining personal privacy and security.