Artificial Intelligence (A) has recently been in the limelight, transforming everything from healthcare to finance. It's also catching the eye of cyber criminals. One question has emerged: Will this new frontier of AI password cracking be the next major challenge for us?
The prospect of AI-powered algorithms predicting or cracking passwords is not merely hypothetical—it's a looming reality. That's a clear and present danger for emails, bank accounts, and other private information.
Join us as we explore this issue and try to shed light on how AI can be leveraged in password cracking. We'll also examine what measures can be taken to secure our digital fortresses in the face of this new threat.
Quick Summary
- AI has been increasingly used to predict and crack passwords, posing potential threats to online security. However, it also provides insights into creating more robust password security mechanisms.
- AI-based research in password security can drastically improve password strength estimators and the overall security landscape.
- PassGAN, a deep learning model, uses generative adversarial networks (GANs) to guess passwords. It has shown a higher success rate in cracking passwords compared to traditional methods.
- While AI's ability to crack passwords presents security concerns, it also aids in developing more robust password policies and systems.
- Strong, unique passwords, two-factor authentication (2FA), and password managers can enhance online security.
How Secure Are Our Passwords?
Passwords are the first defense against unauthorized access to personal and professional data. To comprehend how cybercriminals can leverage AI password cracking, we must first understand how passwords are stored and what makes a password secure.
Storing Passwords: Hashing and Salting
When you set up a password for a website or application, it is not stored in plaintext form that anyone can read. Instead, it undergoes a process known as ‘hashing.' Hashing transforms your password into a unique set of characters known as a ‘hash.'
The most notable thing about hashing is that it's a one-way process. A hash cannot be reversed to find the original password.
To bolster security, many systems also use ‘salting.' The term refers to a random data string added to a password before it is hashed. This makes each hash unique, even if two users have the same password.
Consequently, it becomes much more challenging for attackers to crack the password using precomputed tables of hashes, known as ‘rainbow tables.'
How AI Password Cracking Works
AI, particularly its subset, machine learning, can analyze patterns, learn from data, and make predictions. This ability can be weaponized to crack passwords. Traditional methods like brute force or dictionary attacks can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Conversely, AI can streamline these processes by learning from the patterns in data and making educated guesses.
For instance, by feeding an AI system with a large dataset of leaked passwords, it can learn the common patterns, structures, and sequences people use when creating passwords. With this training, AI password cracking can predict a person's password more accurately than traditional cracking methods.
PassGAN AI Can Crack Your Passwords Perfectly
This isn't a hypothetical scenario. It's something already happening in the real world. Password crackers have been created that far exceed the capabilities of traditional cracking methods. One such example is PassGAN.
PassGAN is a machine learning tool that uses a type of neural network called a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) to generate potential passwords.
The basic idea behind GANs is that they consist of two parts: a generator, which produces data, and a discriminator, which attempts to distinguish between the actual data and the data created by the generator.
The two parts of the GAN compete against each other, leading the generator to produce increasingly convincing data.
In the case of PassGAN, the generator produces strings of characters that it believes might be passwords. Meanwhile, the discriminator is trained on a set of actual passwords and tries to distinguish between these real passwords and those produced by the generator.
Over time, the generator improves at creating strings that look like passwords. The result is a tool that can generate potential passwords, which can be used to test the security of systems.
How Quickly Can AI Crack Your Password?
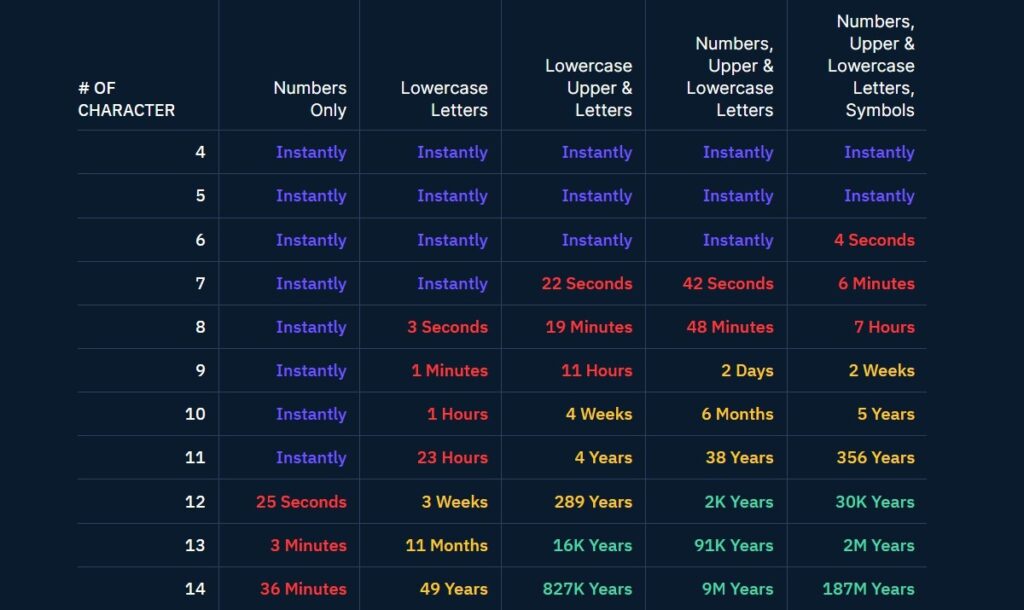
The speed at which an AI can crack your password depends on several factors. These include the complexity and length of the password, the computational power of the AI system, and the specific method used to attempt to crack the password.
Research shows that the most specific passwords between 4 and 6 characters can be cracked instantly. Even a 9-character complex password will take AI two weeks to break. For now, anything beyond complex 11-character passwords will take over 356 years to crack.
If that scares you, let's check out the factors that influence AI password-cracking capabilities;
Password Complexity
Passwords that are longer and use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters are harder to crack because they have a more significant number of possible combinations.
For example, a password with eight characters could have over six quadrillion possible combinations if it uses all four types of characters.
Conversely, a password with the same number of characters but only using lowercase letters has only about 200 billion possible combinations.
Computational Power
The computational power of the AI system also plays a significant role in how quickly it can crack a password. More powerful systems can make more password attempts per second, dramatically reducing the time it takes to crack a password.
For instance, an AI system using a modern GPU could make billions of password attempts per second.
AI Efficiency
Finally, the efficiency of the AI algorithm can affect how quickly a password is cracked. As we've seen with tools like PassGPT and PassGAN, AI password cracking models can be trained to guess passwords more effectively by understanding human password-creation habits and exploiting patterns in data.
This could reduce the time it takes to crack a password, mainly if the password follows common patterns.
How to Reduce the Risk of AI Password Cracking
As we've seen, AI password cracking doesn't just work at specific levels. It provides an overall boost to password cracking attempts. AI algorithms can crack even the most complex passwords as they get more efficient. This ability, while alarming, is a call to action for more robust password creation and management.
Unique passwords for each online account are recommended, combining numbers, letters (uppercase and lowercase), and special characters. Longer passwords are also more secure – passwords with 12 or more characters are considered safer.
Other measures to take include;
Leveraging Password Managers
Password managers can help create and store complex passwords. They generate long, random passwords for your online accounts and store them securely, so you don't need to remember each one. All you need to remember is the master password.
Naturally, One vital caveat is choosing a reputable password manager. The LastPass debacle has shown us that some brands cannot be trusted with our security. Some reputable password managers include;
1Password: This password manager is known for its user-friendly interface and robust security. 1Password allows you to store various information, including logins, credit card details, and secure notes.
NordPass: This service is a relatively new player in the password manager field. However, it's built by the same team behind NordVPN, one of the most reputable VPN brands. NordPass offers a clean, user-friendly interface and strong security features.
Bitwarden: If you're a fan of open-source apps, then give Bitwarden a go. It's a password manager known for its transparency and affordability. It offers a free version with unlimited password storage, syncing across all devices, and two-factor authentication.
Two-Factor Authentication
Enabling Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts. Even if your password is compromised, an attacker would still need access to the second factor—usually a piece of information only you have, like a physical device or access to an email account—to gain entry.
Try working with some universal 2FA apps that can integrate your security needs into a single dashboard. Examples include;
Google Authenticator: This free app from Google generates 2FA codes on your smartphone. It works even if your device doesn't have an internet connection.
Microsoft Authenticator: Like Google Authenticator, Microsoft's version generates 2FA codes. It offers additional features such as push notifications for approval and a backup feature to move your accounts between different devices easily.
Authy: Authy provides a more user-friendly interface and features than other apps. One significant benefit of Authy is that it allows for multi-device syncing, meaning you can access your codes on multiple devices.
Regular Password Changes
Regularly updating your passwords can limit the damage if they are somehow compromised. While it may seem tedious, this practice is crucial in maintaining robust online security. Some services are starting to enforce mandatory password change schedules, but you'll have to do it yourself for now, most of the time.
Awareness and Education
Finally, awareness and education about potential threats and security best practices can significantly reduce the likelihood of password-related breaches. Individuals and organizations must stay informed about the evolving threat landscape and learn how to protect themselves effectively.
How AI Can Help Improve Password Security
As AI continues to evolve, it could help develop more secure alternatives to traditional passwords. Biometrics, for instance, are already used in many devices and services as a form of authentication.
AI can help improve the accuracy and reliability of biometric systems, making them more secure and user-friendly. Facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice recognition are some examples of where AI can significantly improve security.
AI for Predicting and Preventing Breaches
AI can also be used to predict and prevent security breaches. By analyzing patterns in data, AI systems can identify unusual activity that might signify a breach. This could involve detecting multiple failed login attempts, identifying suspicious patterns of behavior, or even predicting which users are likely to be targeted by attackers.
Quantum Computing and Cryptography
Quantum computing, while still in its infancy, could significantly affect the future of password security. Quantum computers could crack even the most secure encryption methods used today. However, they could also lead to the development of newer, more secure forms of encryption.
AI will likely play a critical role in these developments, helping to create and manage quantum encryption methods.
Continuous Authentication
AI could also enable continuous authentication, where the user is authenticated not just at login but continuously throughout their session based on behavior patterns. This could include typing speed, mouse movements, or user interaction with the interface.
Will AI Password Cracking Really Be a Cat-and-mouse Game?
Advancements in AI pose a significant threat to password security. While AI algorithms have become more sophisticated and robust, so have the techniques employed by cybercriminals to crack passwords.
However, it is essential to note that AI password cracking is a double-edged sword. It not only fuels the development of more potent cracking methods but also enables the creation of robust defense mechanisms.
The battle between AI-powered password crackers and AI-driven security measures will likely intensify, leading to a continuous cat-and-mouse game in cybersecurity. Individuals and organizations must remain vigilant, adopt strong passwords, and leverage AI to fortify their digital defenses against evolving threats.