The Internet today is a dangerous place to be without some safeguards in place. Cybercriminals go to extreme levels to steal information, and trojan malware is one of their most formidable tools. These nasty parasites can do everything from taking control of our devices to sending all our private information to attackers.
Forewarned is forearmed, and learning more about Trojans can give you an edge in staying safer online.
Protect Your Digital Privacy With NordVPN
NordVPN lets you hide behind its secure servers and encrypts all your data. Stay safe from cybercriminals and websites that track your online activities.
What is a Trojan?
A Trojan is a malicious software designed to perform a specific function or set of tasks without the user's knowledge or consent. Trojans are often disguised as legitimate software or delivered through email attachments or links to malicious websites.
Once a Trojan is installed on a computer, it can perform a variety of tasks, such as:
- Downloading and installing additional malware on the computer.
- Collecting sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial data.
- Modifying system settings or system files.
- Displaying unwanted or malicious ads.
- Redirecting the user's web browser to malicious websites.
- Allowing unauthorized access to the infected computer by an attacker.
How Trojans Work
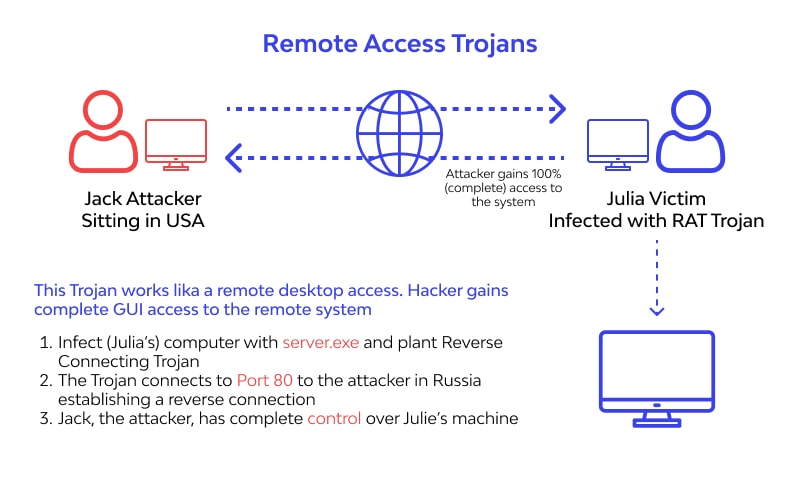
Unlike viruses and worms, Trojans do not replicate themselves or spread to other computers. Instead, they rely on the user to take some action. It can be anything from clicking a link or downloading an attachment. Once the action occurs, the Trojan will deploy on the device.
There are several ways that Trojan malware can be delivered and installed on a computer. Some typical methods include:
- Email attachments: Trojans can be disguised as legitimate email attachments, such as documents or images, and delivered to the user through spam emails or phishing scams. Once the user downloads and opens the file, the Trojan installs itself.
- Malicious websites: Trojans can come from malicious websites designed to exploit vulnerabilities in the user's web browser or operating system. The Trojan is automatically downloaded and installed on the computer when the user visits the website.
- Software downloads: Trojans can be bundled with legitimate software downloads and installed along with the software. This silent installation often happens without your knowledge or consent.
Once the Trojan is installed on the computer, it can perform various tasks, such as downloading and installing additional malware, collecting sensitive information, modifying system settings, displaying unwanted or malicious ads, and redirecting the user's web browser to malicious websites.
In some cases, the Trojan may also create a “backdoor” on the infected computer, allowing an attacker to remotely access and control the computer. With this access, cybercriminals can steal information, disrupt the operation of the computer, or use the computer to attack other systems.
How to Recognize and Detect a Trojan
To detect a Trojan, you can use a reputable antivirus program to scan your device for malware. Most antivirus programs can detect and remove Trojans and other types of malware.
You can also manually check your device for Trojans by looking for unfamiliar programs or icons, checking for unusual network activity, and examining your device's startup programs.
It is important to regularly scan your device for Trojans and other types of malware to ensure it is free from infections. It is also a good idea to keep your antivirus software updated to ensure it can detect the latest threats.
There are several signs that you may have a Trojan on your device:
- Unfamiliar programs or icons: If you see strange programs or icons on your device, it could be a sign that a Trojan has been installed.
- Slow performance: Trojans can use up system resources and cause your device to slow down.
- Unwanted pop-ups or ads: Trojans can display unwanted pop-ups or ads on your device.
- Unfamiliar or unexpected behavior: If your device behaves in an unfamiliar or unexpected way, it could be a sign that a Trojan is present.
How to Remove Trojan Malware
To remove Trojan malware from your device, you can follow these steps:
- Disconnect from the internet: Disconnecting from the internet can help prevent the Trojan from communicating with its command and control server and prevent it from downloading additional malware.
- Run a scan with a reputable antivirus program: Use a reputable antivirus program to scan your device for Trojans and other types of malware. Most antivirus programs can detect and remove Trojans and other types of malware.
- Delete any suspicious files: If the antivirus scan identifies any suspicious files, delete them.
- Use a malware removal tool: Sometimes, you may need an online malware removal tool. Many cybersecurity companies offer these services for free, such as the Avast Malware Scanner and Remover.
- Restart your device: After removing the Trojan, restart your device to complete the removal process.
- Change your passwords: If the Trojan could steal them, it is essential to change them to prevent unauthorized access to your accounts.
10 Common Types of Trojan
Trojans are a mature form of malware and have undergone heavy development. Many variants are floating around in cyberspace today. Some common types of trojan include;
- Banker Trojans steal financial information, such as login credentials and bank account numbers.
- Cryptojacking Trojans help cybercriminals mine cryptocurrency on infected devices secretly.
- Downloader Trojans download and install additional malware on the infected computer.
- Infostealer Trojans steal data such as login credentials and financial data.
- Ransomware Trojans encrypt files or entire hard drives remotely. The victim can only regain access by paying a ransom to the attackers, who provide a decryption key in exchange for money.
- Remote Access Trojans (RATs) are used to gain unauthorized access to the infected computer and control it remotely.
- Rootkit Trojans help attackers gain root or administrator access to the infected computer, allowing them to hide their activities and gain complete control of the system.
- Spyware Trojans collect sensitive information, such as login credentials and browsing history, without the user's knowledge.
- Banking Trojans steal financial information, such as login credentials and bank account numbers.
- Virus-Making Trojans create and distribute viruses and other types of malware.
Examples of Significant Trojan Malware Attacks
Although most trojan malware attacks are piecemeal, that doesn't mean they're unable to wreak havoc on a broad scale. There have been many examples of trojan attacks that have crippled entire networks or information clusters.
Examples of these large-scale trojan attacks include;
Emotet Trojan
Emotet is a sophisticated banking Trojan first detected in 2014. It has evolved and is known for its ability to evade detection and spread rapidly through networks. The Emotet trojan was involved in numerous high-profile attacks, including a 2018 attack that disrupted operations in the City of Allentown, Pennsylvania.
BlackEnergy Trojan
Attackers have used BlackEnergy in several high-profile attacks, including the 2015 Ukrainian power grid attack and the 2017 NotPetya ransomware attack. It is known for its ability to evade detection and exploit vulnerabilities in industrial control systems (ICS).
Flame Trojan
Flame is a highly sophisticated Trojan malware discovered in 2012. Some believe a nation-state developed Flame to target individuals and organizations in the Middle East. Flame is known for its ability to collect sensitive information and exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks.
What Devices Can Trojans Infect?
Because there are so many trojan variants, few devices are immune to trojan attacks. Although most trojans target specific platforms, there's something for almost everything today.
These are devices currently known to be vulnerable to trojan attacks;
Desktops and laptops: Trojans can infect computers running Windows, macOS, Linux, and other operating systems.
Mobile devices: Trojans can infect smartphones and tablets running Android, iOS, and other mobile operating systems.
Network devices: Trojans can infect routers, switches, and other network devices.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices: Trojans can infect smart devices, such as smart TVs, smart thermostats, and smart security cameras.
Industrial control systems (ICS): Trojans can infect devices used in industrial environments, such as supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems and programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
How to Protect Yourself Against Trojans
There are several ways to protect your devices from Trojans and other types of malware:
Use a Reputable Antivirus Program
A good antivirus program can help detect and remove Trojans and other types of malware. Make sure to keep your antivirus software up to date to ensure that it can protect against the latest threats.
Some VPNs today include threat detection capabilities that are maturing in ability. Because of that, these tools have proven to be an excellent second line of defense against malware attacks. One good example is NordVPN's Threat Detection feature.
Be Wary of Opening Email Attachments or Links
Trojans can be delivered through email attachments or links to malicious websites. Be wary of emails from unknown sources, and do not open attachments or click on links unless you are sure they are safe.
Keep Apps Updated
Software updates often include security patches that can help protect against new threats. Make sure to keep your operating system and other software up to date to ensure that you have the latest protection.
Use a Firewall
A firewall can help block incoming traffic from unknown sources, which can help prevent Trojans and other types of malware from entering your network.
Use Strong, Unique Passwords
Weak or easily guessable passwords can make it easier for attackers to gain access to your accounts. Use strong, unique passwords, and consider using a password manager to help keep track of them.
Although I use LastPass, it has come under scrutiny now, thanks to a data breach of its systems. However, NordPass is an excellent alternative currently going for a reasonable price.
Enable Two-factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring a second form of authentication, such as a code sent to your phone and your password. This can help prevent unauthorized access to your funds, even if your password is compromised.
Final Thoughts – Prevention is Better Than Cure
You should protect your devices from Trojans and other types of malware by using a reputable antivirus program and being cautious when downloading or opening email attachments or links. You should also keep your operating system and other applications updated, as these updates often include patches that address new-found vulnerabilities.
Also Read;